BSA & Galexia Global Coud Computing Scorecard (2018) - Galexia Analytics Release
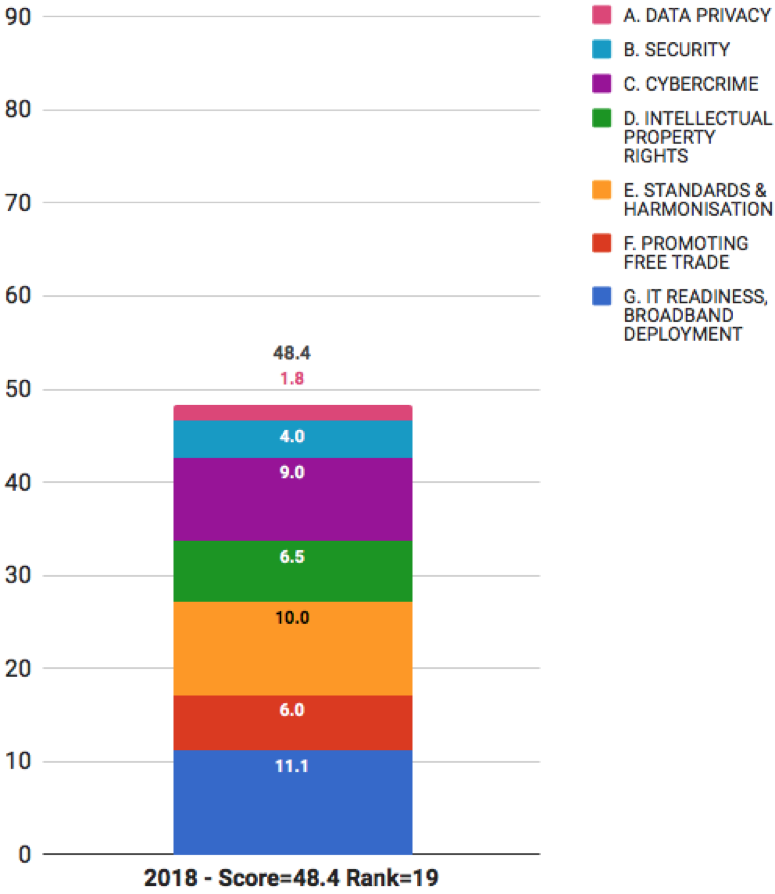
2018 Rank 19. Thailand - Score: 48.4 | Change from 2016 - Rank: +2
Thailand’s laws and policies in relation to cloud computing and the digital economy are patchy, with strengths in some areas and significant gaps and weaknesses in others.
Thailand has implemented comprehensive cybercrime legislation, which helps to enhance confidence in information technology (IT). Thailand also has good laws for electronic commerce and electronic signatures. However, Thailand has no privacy laws, and this is a major weakness.
In January 2015, two Copyright Amendment laws were approved: the Copyright Act (No. 2) B.E. 2558 (A.D. 2015), and Copyright Act (No. 3) B.E. 2558 (A.D. 2015). These two new laws implement many of the key provisions of the WIPO Copyright Treaty. They also introduced an Internet service provider (ISP) liability scheme for copyright infringements that applies in broad circumstances.
Additional risks in Thailand include mandatory Internet censorship (some of which is clearly political in nature) and filtering, and procurement preference policies.
Overall, Thailand’s position in the Scorecard rankings has risen slightly since 2016 — from 21st to 19th — mostly because of incremental improvements in the Cybercrime and Intellectual Property Rights sections. Improvements in the IT readiness and broadband Developments based on the Thailand Digital Economy and Social Development Plan 2016 are also ongoing.
The rank for Thailand in this year's Scorecard is:
- 19th overall,
- 20th for legal and policy, and
- 17th for IT readiness and broadband deployment.
Within legal and policy themes for cloud readiness Thailand has the following rankings:
- 23rd for data privacy
- 19th for security
- 17th for cybercrime
- 14th for intellectual property rights
- 13th for standards and international harmonization
- 17th for promoting free trade
View the Country Report (PDF) »
![[ Galexia Dots ]](/images/hr.gif)
![[Data protection regulations and international data flows: Implications for trade and development (April 2016)]](/public/ssi/pubs/pub_6.png)
 print this page
print this page sitemap
sitemap rss news feed
rss news feed manage email subscriptions
manage email subscriptions