BSA & Galexia Global Coud Computing Scorecard (2018) - Galexia Analytics Release
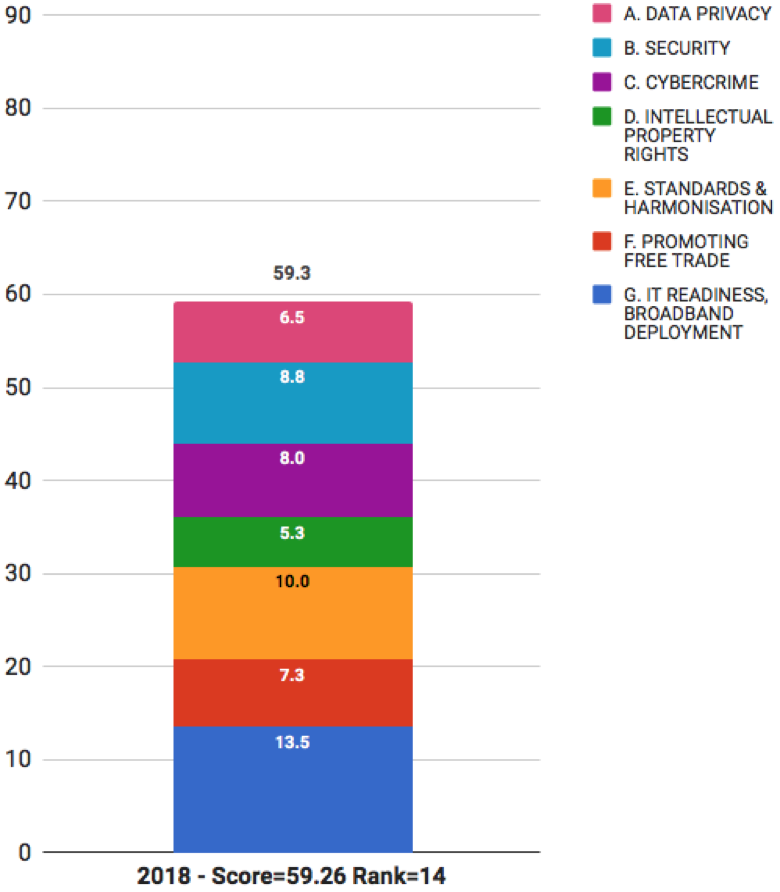
2018 Rank 14. Malaysia - Score: 59.26 | Change from 2016 - Rank: -1
Malaysia has modern electronic signature laws, and electronic commerce laws in place. These measures provide good level of protection for computing in Malaysia.
Malaysia has data protection regulation in place that is generally compatible with globally recognized frameworks. However, the law does not include data breach notification provisions and data controllers are required to register with the Personal Data Protection Department.
Malaysia has specific provisions in place for law enforcement access to encrypted data that, in some instances, may act as de facto mandate for the use of specific security technology.
Malaysia’s copyright laws are aligned with international standards, although enforcement remains patchy.
Malaysia has a moderate level of broadband penetration. In 2015, the government committed to new broadband targets: by 2020, 100 percent of households in capital cities and high-impact growth area to have access to speeds of 100 Mbps and 50 percent of households in suburban and rural areas to have access to speeds of 20 Mbps.
Malaysia fell slightly in the Scorecard rankings — from 13th place in 2016 to 14th place in 2018.
The rank for Malaysia in this year's Scorecard is:
- 14th overall,
- 15th for legal and policy, and
- 14th for IT readiness and broadband deployment.
Within legal and policy themes for cloud readiness Malaysia has the following rankings:
- 16th for data privacy
- 11th for security
- 20th for cybercrime
- 22nd for intellectual property rights
- 13th for standards and international harmonization
- 14th for promoting free trade
View the Country Report (PDF) »
![[ Galexia Dots ]](/images/hr.gif)
![[Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) for Cooperative Intelligent Transport System (C-ITS) data messages]](/public/ssi/pubs/pub_3.png)
 print this page
print this page sitemap
sitemap rss news feed
rss news feed manage email subscriptions
manage email subscriptions